Physiotherapy

Alleviating and preventing pain
Physical therapists use approaches to eliminate neuropathic pains and discomfort associated usually with acute neurological conditions and nociceptive/musculoskeletal pain that ensues as a secondary complication in various chronic neurological diseases.
Promotion of neuroplasticity
Physical therapy promotes neuronal plasticity and aids in healing by encouraging the brain to remodel itself through carefully planned task-oriented exercises, that is to be performed actively and repeatedly by the patient. Reduction in spasticity: Physiotherapists use methods to prevent occurrence of spasticity or control spasticity in order to increase muscle elasticity, lessen pain, and facilitate movement.

Reduction in spasticity
Physiotherapists use methods to prevent occurrence of spasticity or control spasticity in order to increase muscle elasticity, lessen pain, and facilitate movement.
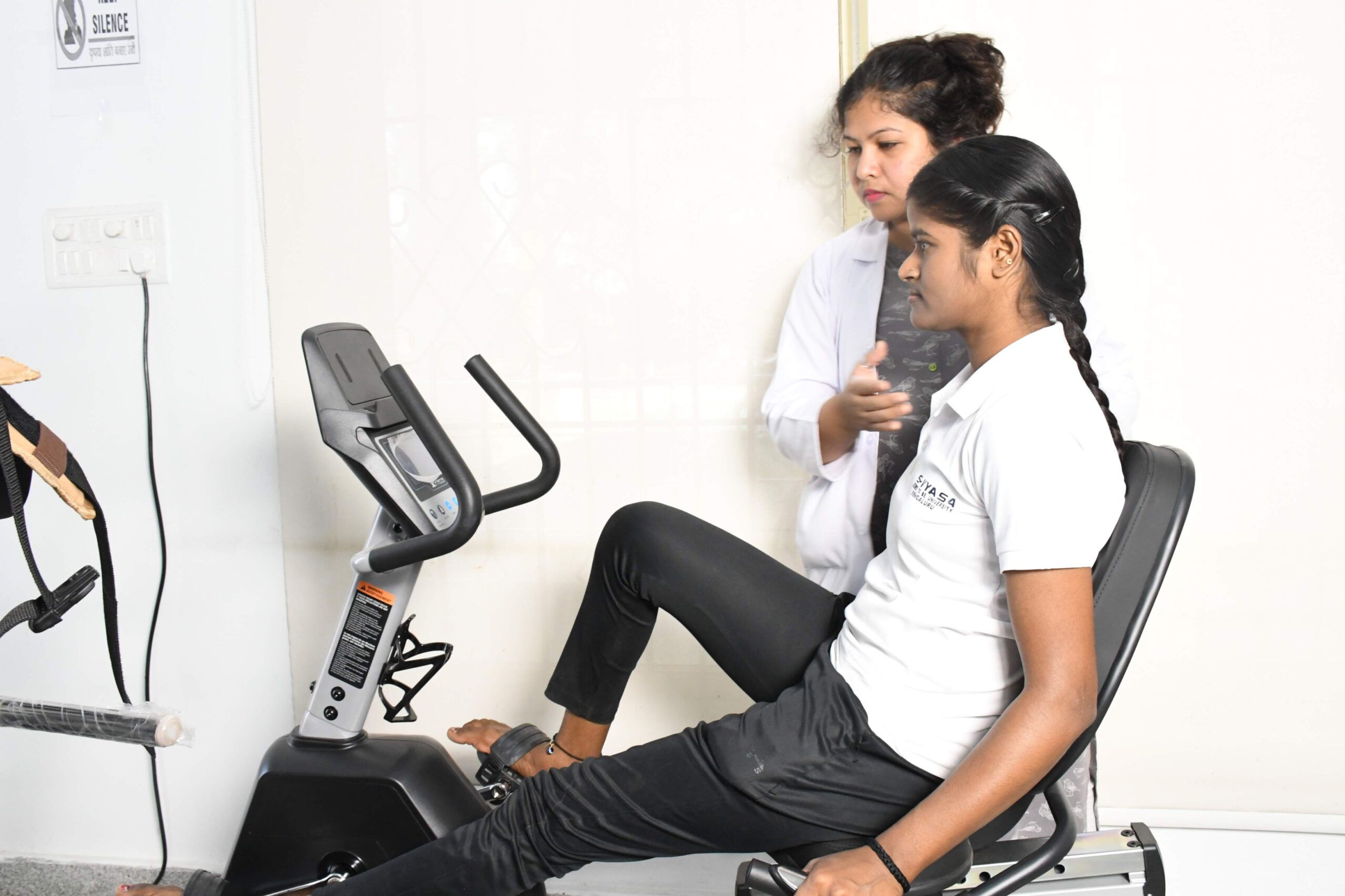

Improvement in cardio-vascular endurance
A compromised cardio-vascular health can be improved with mild intensity and high repetition aerobic training based on the status of the disease and requirement of the individual.
Restoring muscle strength
Targeted exercises and techniques aid in the strengthening of inadequate muscles, which often require support for even the most fundamental activities of daily living, thereby boosting total physical strength and endurance.
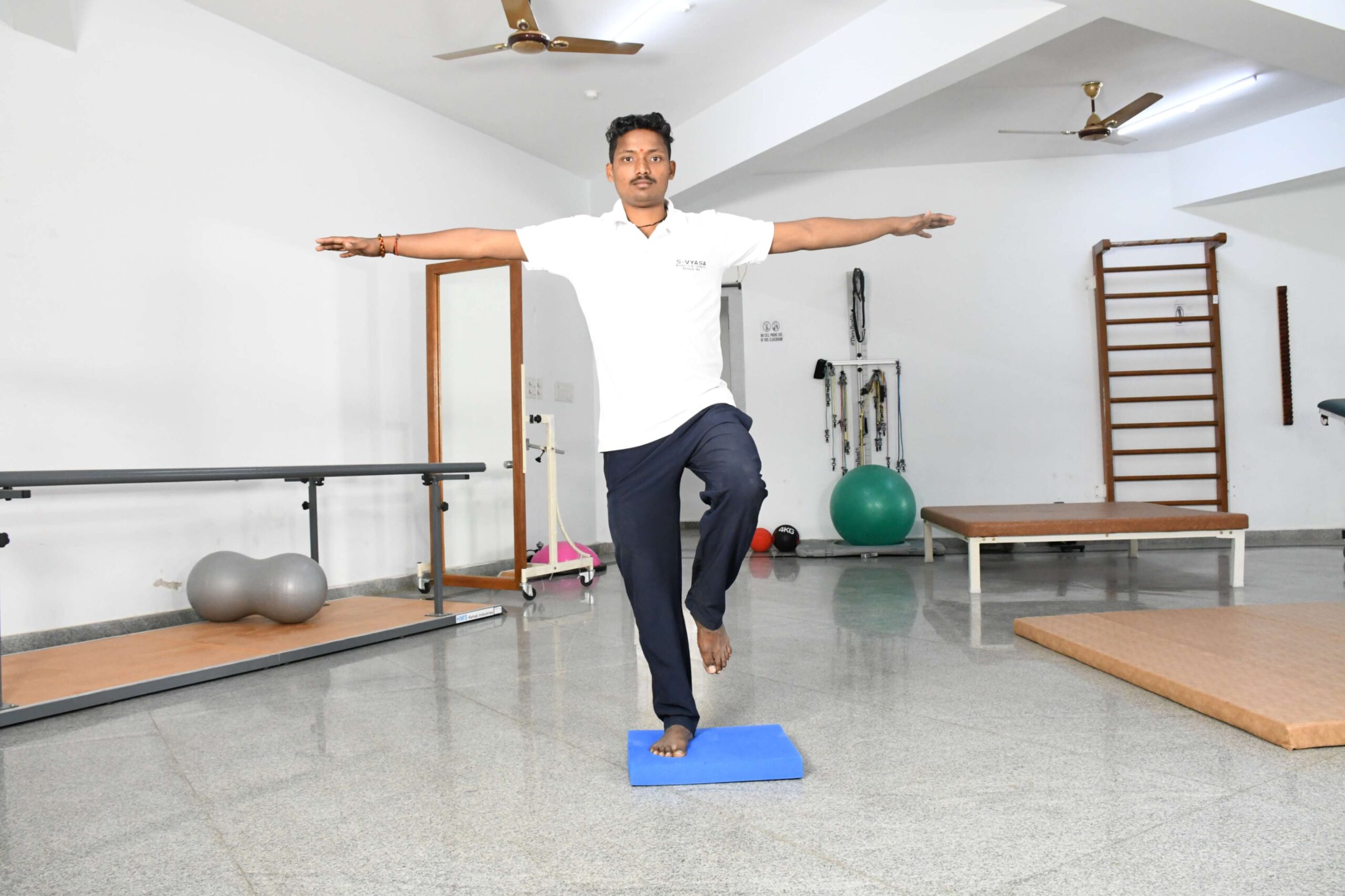

Enhancing balance and coordination
Physiotherapy interventions aim to improve balance and coordination, to train and individual adapt to the challenges of a dynamic environment and to perform the activities of daily living without and assistance, supervision or fear, hence lowering the risk of falls and injuries.

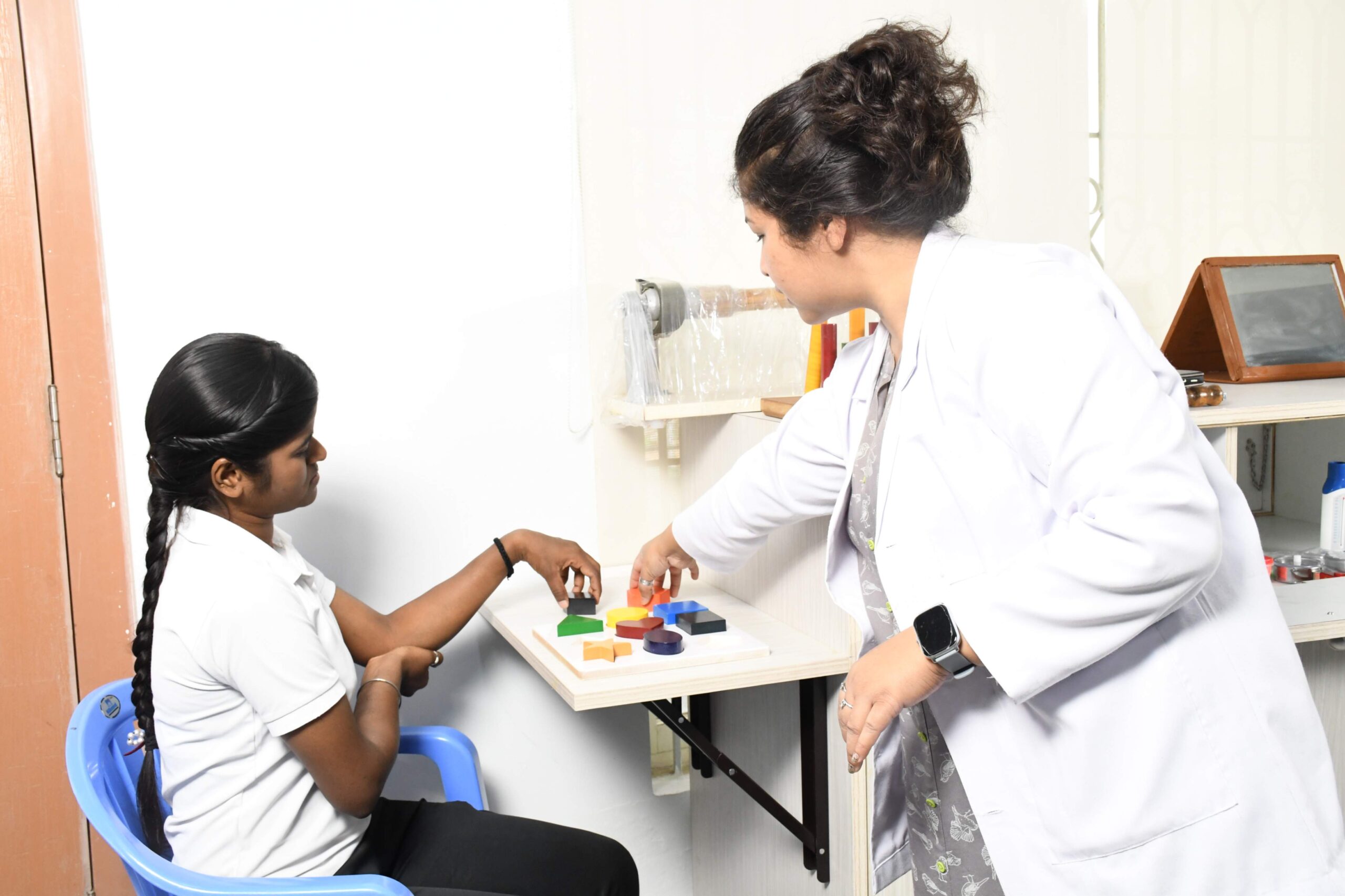
Stimulating cognitive functions
It entails exercises that test cognitive abilities, enhance physical recovery, and increase executive functions of brain such as inhibition control, attention, processing and registering of information, memory, analysis, reasoning, problem-solving, planning and executing.
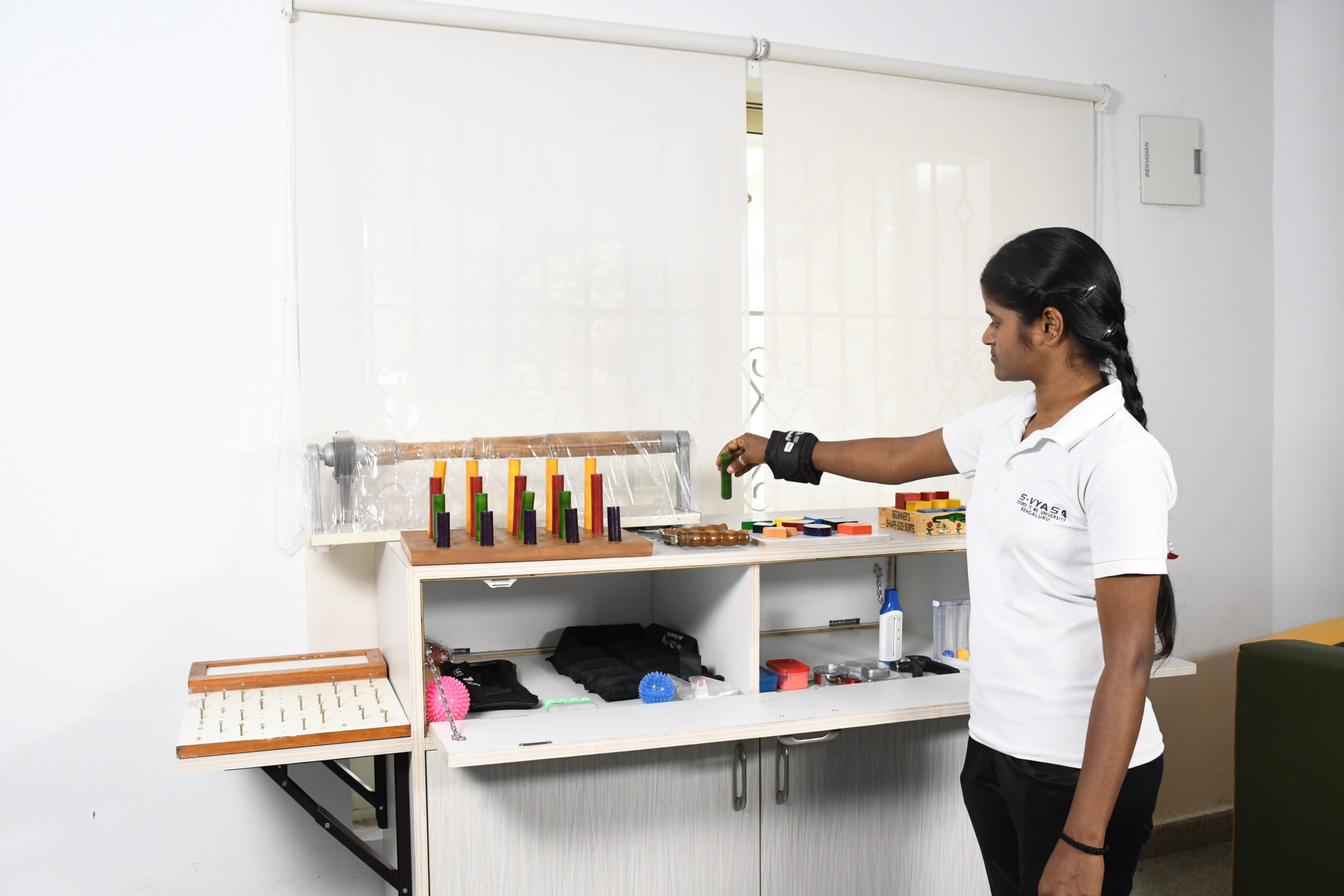

Educating and prevention of secondary complications
Secondary complications such as pressure sores, UTIs, atrophy, spasticity, contractures, deformity, cardiac and respiratory issues can be avoided primarily by practice of preventive measures right from the acute stage of the disease.

Regaining mobility
Physical therapy assists people in regaining mobility, allowing independence in activities of daily living. Independence in mobility can be achieved by unaided mobility or aided mobility with sticks, canes, crutches, walkers, rollators, prosthetic limb or wheelchairs.
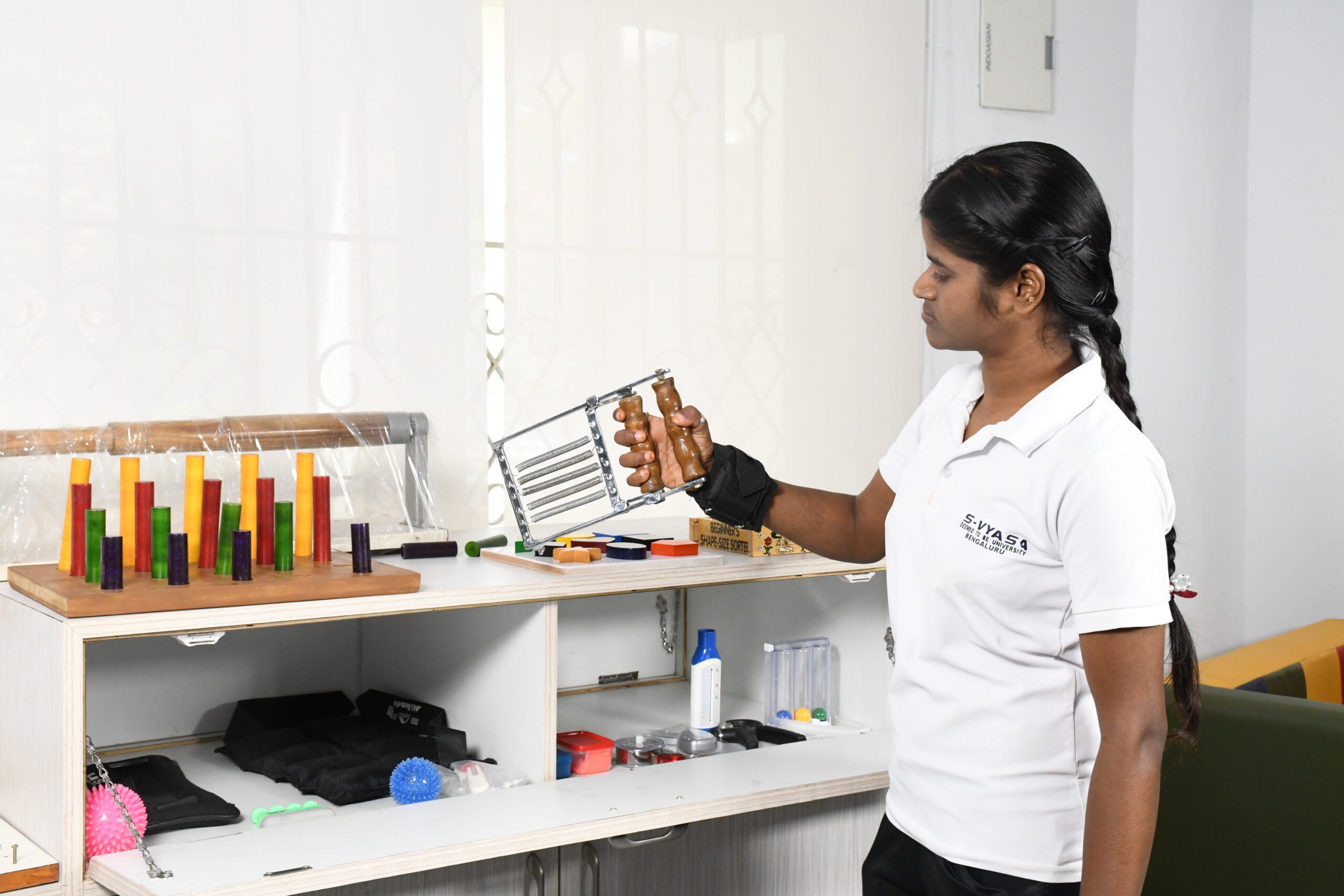

Improvising social interaction, confidence and emotional wellbeing
The supportive environment of therapy sessions fosters a sense of community and belonging, which can be especially beneficial for those living with neurological issues.
Improved quality of life
Physical rehabilitation improves the complete physical, mental and social well-being of the individual who has been previously dependent for all the aspects of life. Improvement in quality of life also encourages and an individual to live a financially independent and a dignified life in the society.
In neurological rehabilitation, physical therapy involves a variety of treatments intended at improving mobility, balance, and overall functional capacity. These techniques are carefully chosen based on the state and progress of the patient. Among the most regularly utilized techniques are
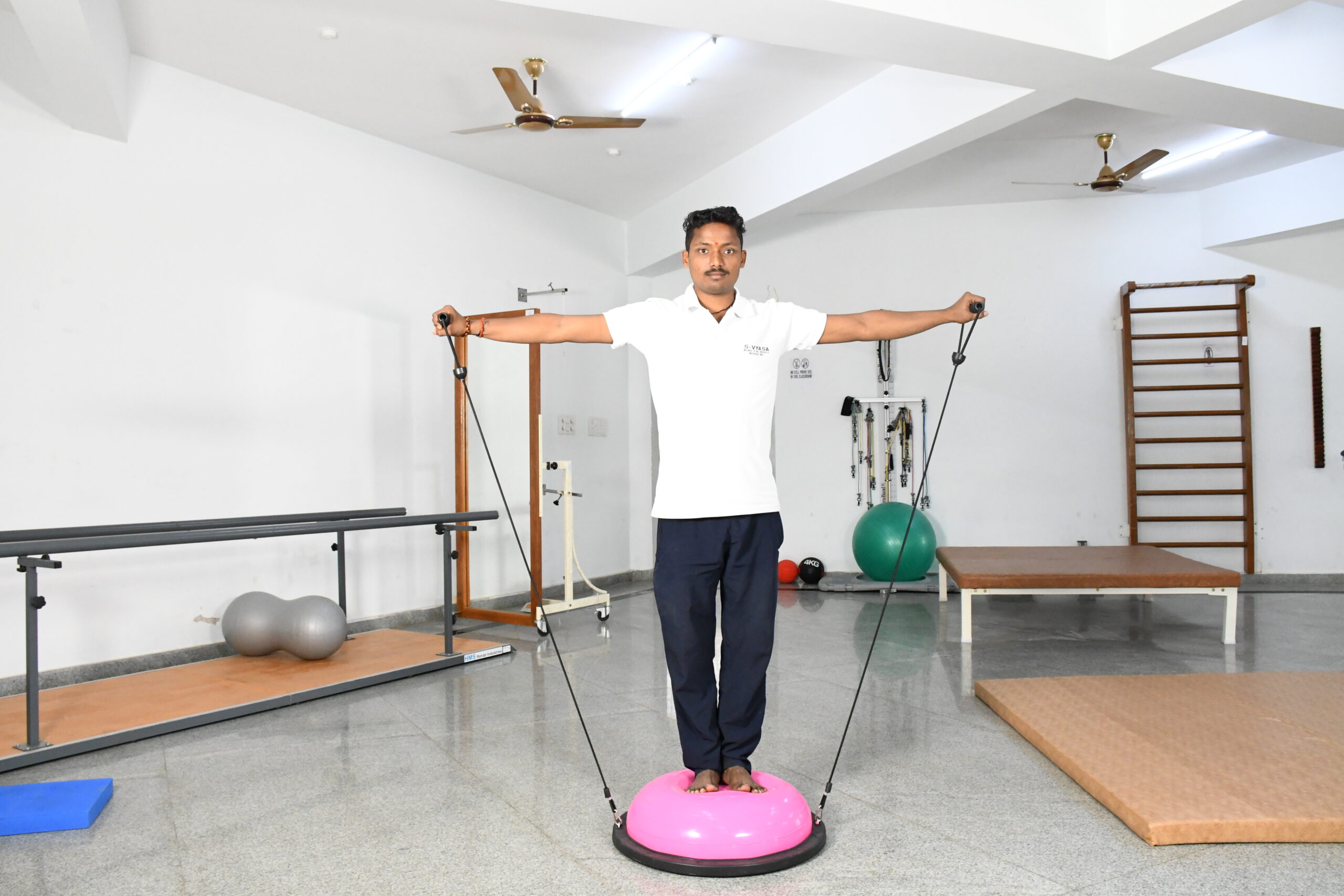

Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (CIMT)
This treatment includes restricting the use of the unaffected limb in order to encourage the usage and recovery of the affected leg, hence improving motor skills and coordination.
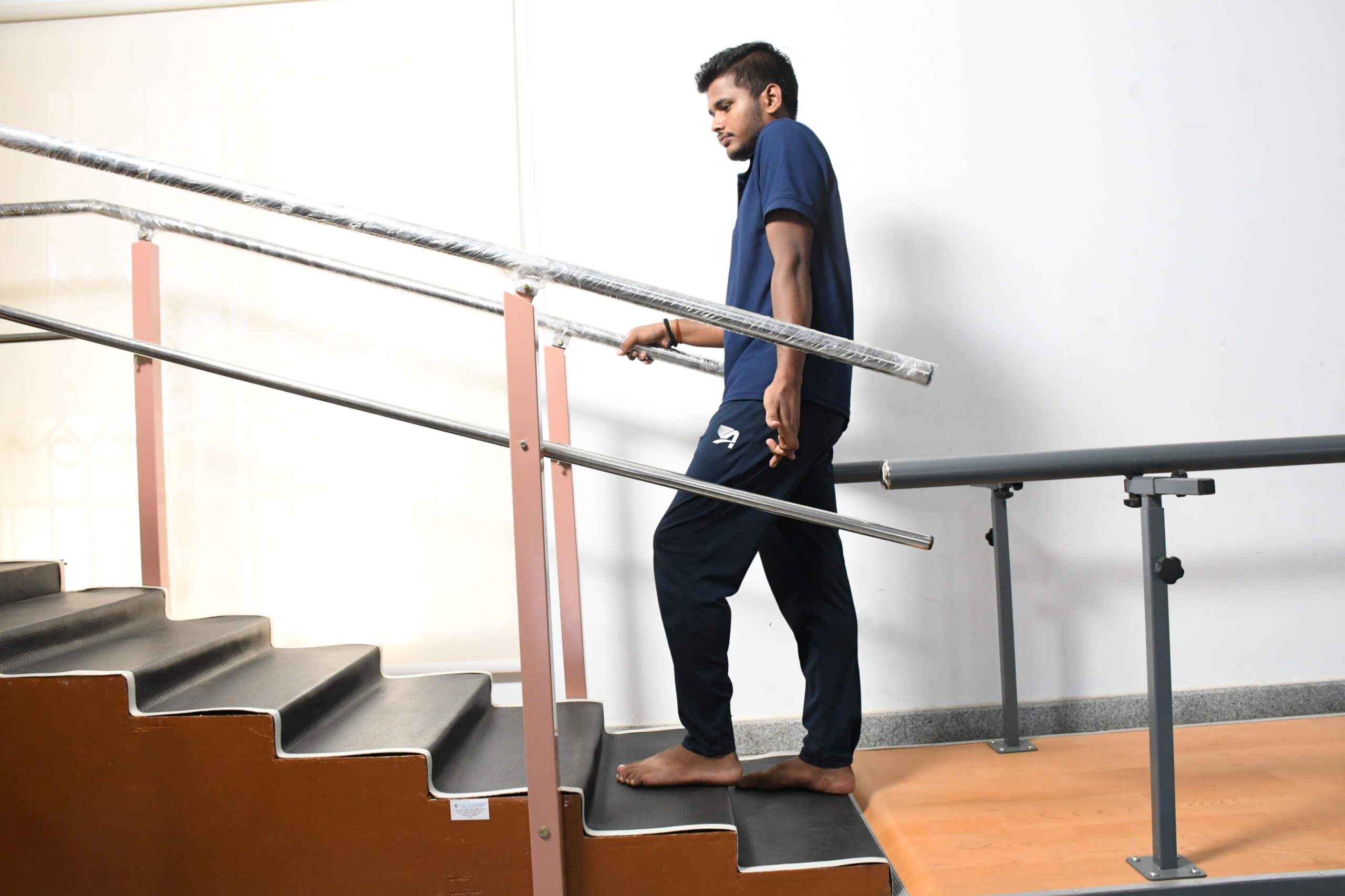
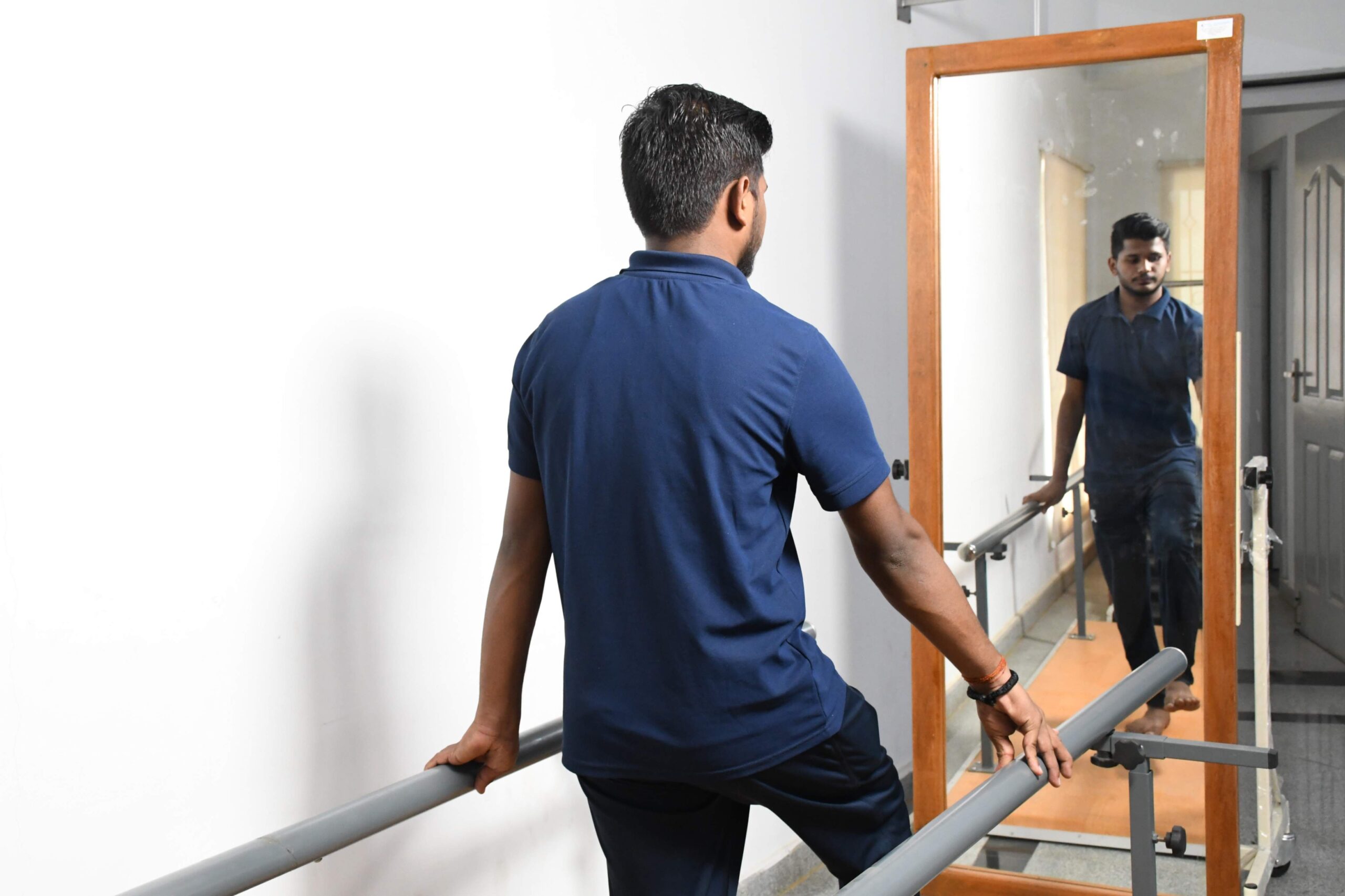
Gait Training
Physiotherapists work on correcting walking patterns and improving balance to improve a patient's ability to walk independently.
FES (Functional Electrical Stimulation)
FES is the use of electrical currents to stimulate weaker muscles, encouraging muscular contractions and enhancing strength and function.
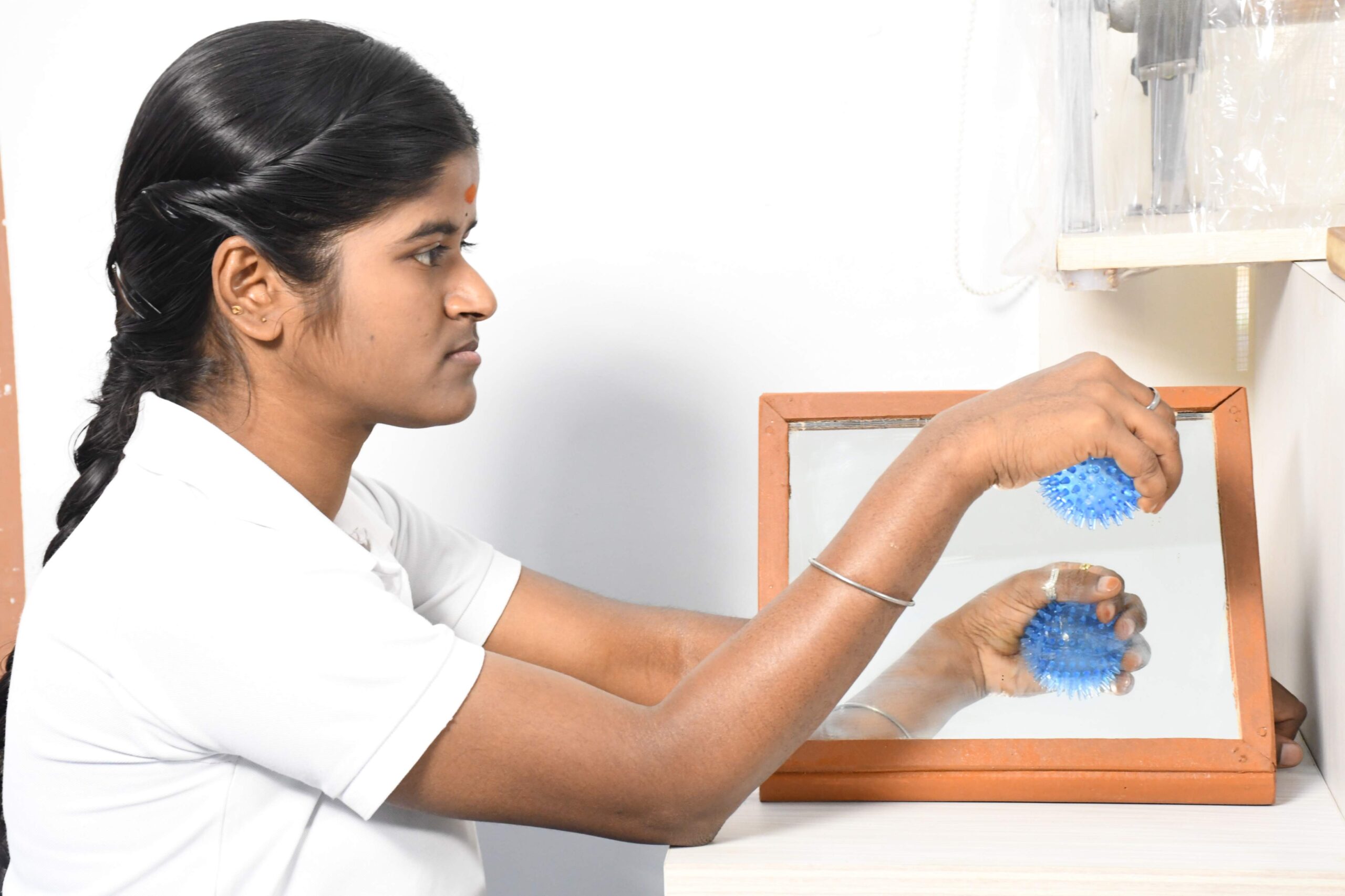

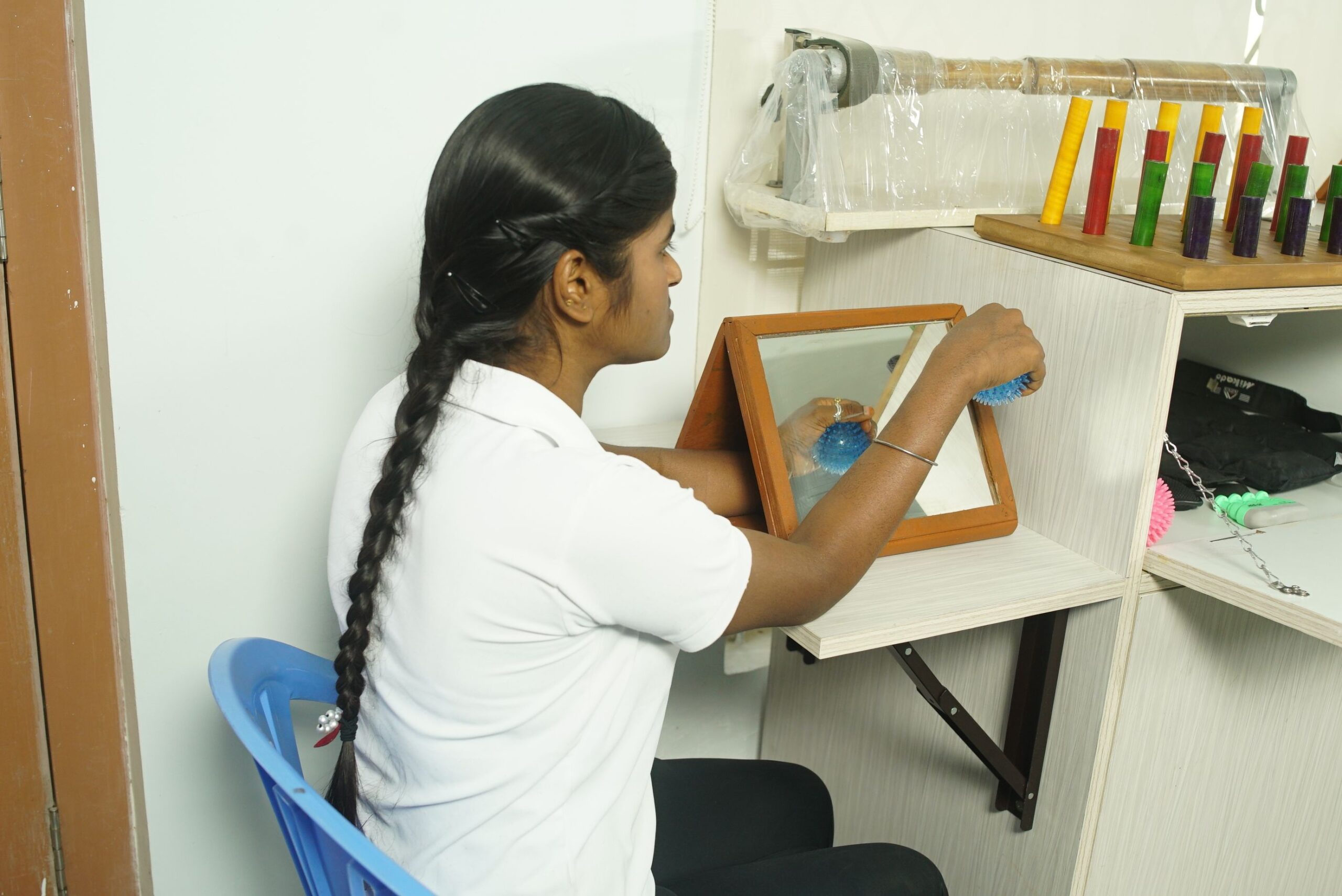
Mirror Therapy
Mirror therapy uses a mirror to provide the impression that the afflicted limb is moving normally. In circumstances such as stroke-related hemiparesis, this method can assist improve motor function and alleviate pain.
Task-Specific Training
Patients engage in activities that mimic real-life duties, assisting them in regaining functional abilities and fostering brain reorganization.
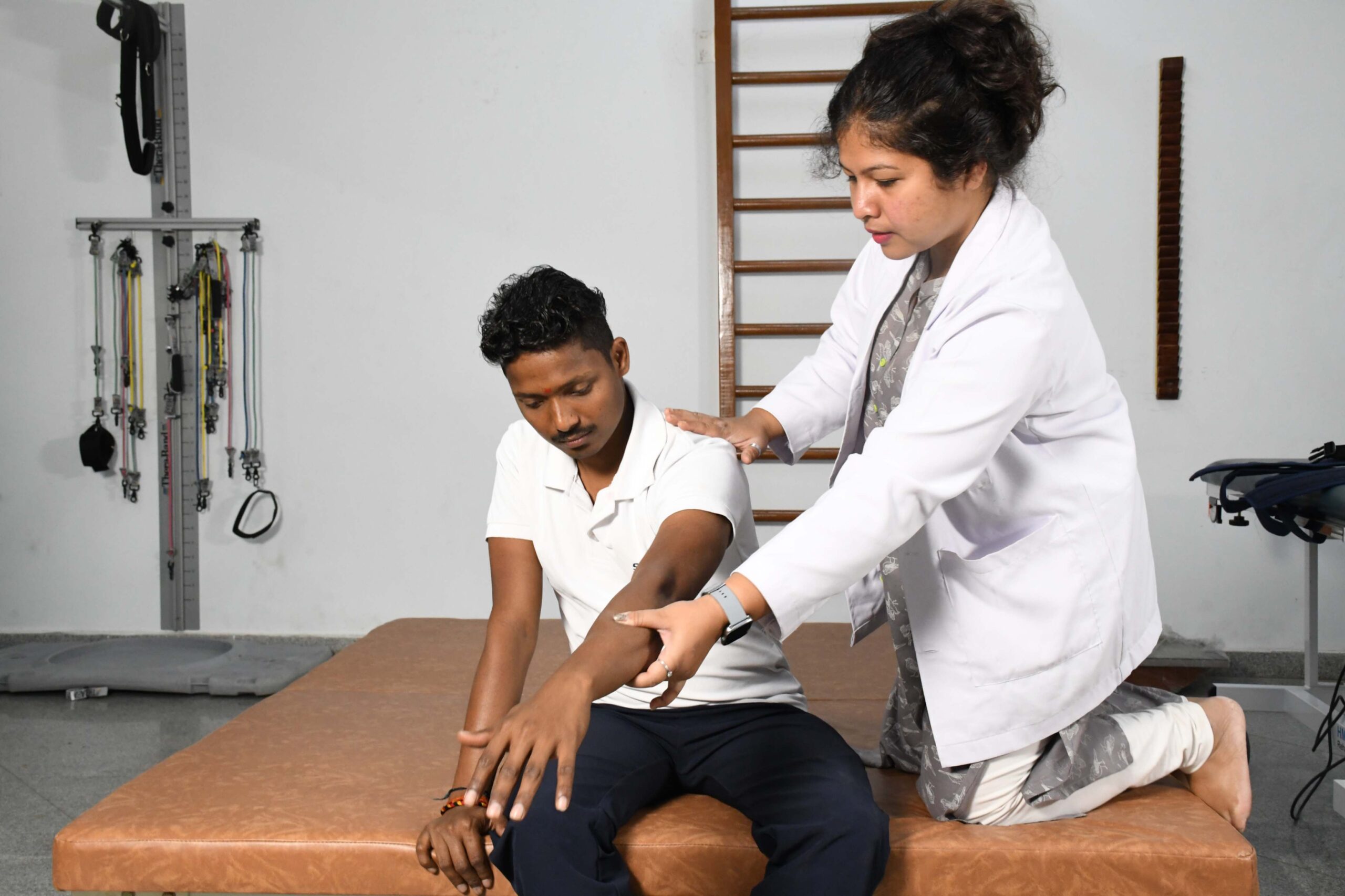
Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF)
PNF treatments incorporate precise muscle group movement patterns and stretching. This method aids in the improvement of muscle coordination, strength, and flexibility.
Training in Virtual Reality (VR)
Virtual reality technology is rapidly becoming prevalent in neurological rehabilitation. VR physical activity present patients with an interesting and immersive environment in which to practice motions, enhance coordination, and regain functional skills in a controlled setting.
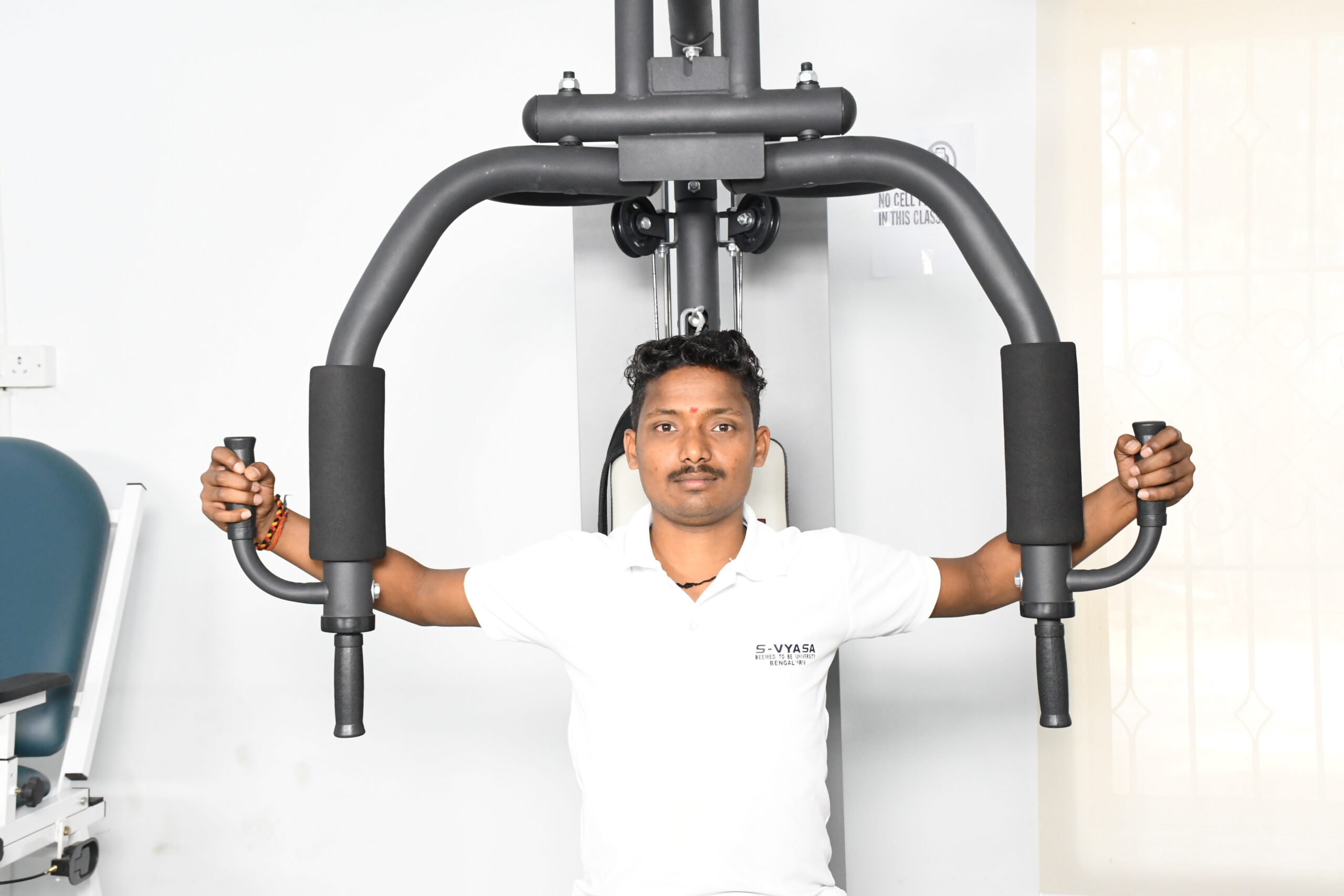

Range of Motion Exercises
Gentle motions that aid in the maintenance of joint flexibility and the prevention of stiffness.
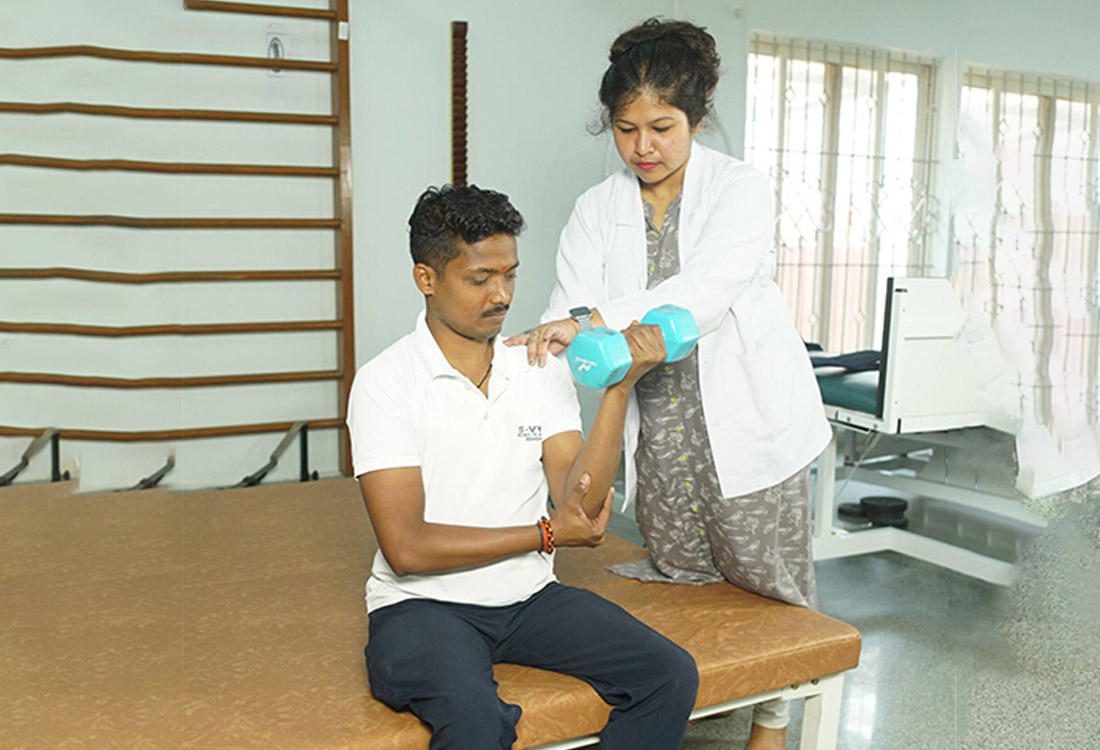
Strength Training
Specific exercises designed to increase muscle strength and functional capabilities.
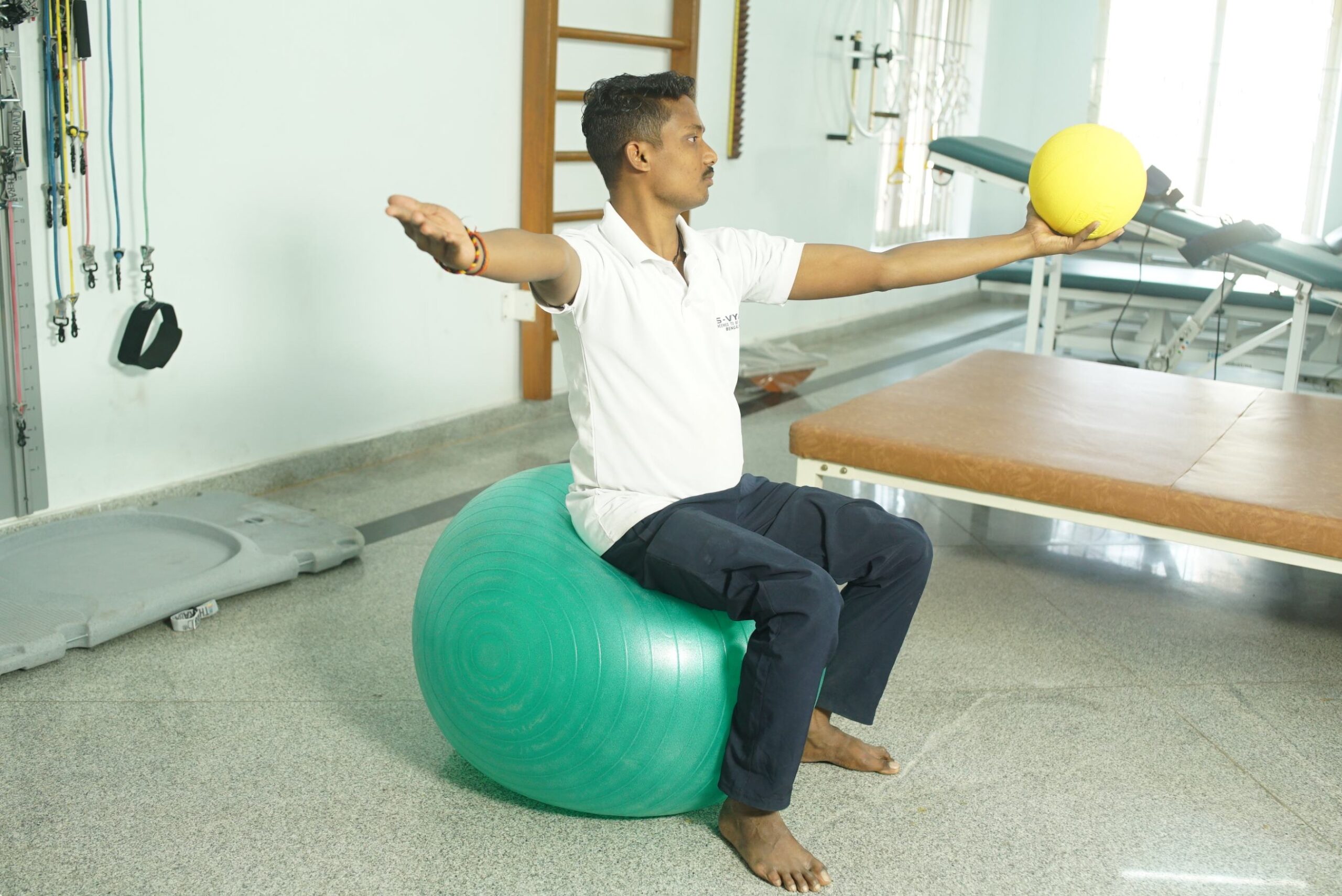

Balance and Coordination Exercises
Activities that challenge balance and coordination and aid in the recovery of persons.
Functional Tasks Practice
Participating in activities that one performs in daily life, such as dressing, cooking, or using utensils to develop independence.

Aquatic Therapy
Water-based training sessions promote mobility and muscular strengthening.

Tens
Neuropathic pains include stabbing, burning, tingling type of pain which can particularly disturb the individual throughout the day. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation works by effectively blocking the pain signals from peripheral nerve fibres from transmitting via the spinal cord to reach the brain. TENS therapy also stimulates the production of body's natural pain killers i.e endorphins which also contributes in relieving the nerve pain common in conditions like polyneuropathy, diabetic neuropathy and peripheral neuropathy.
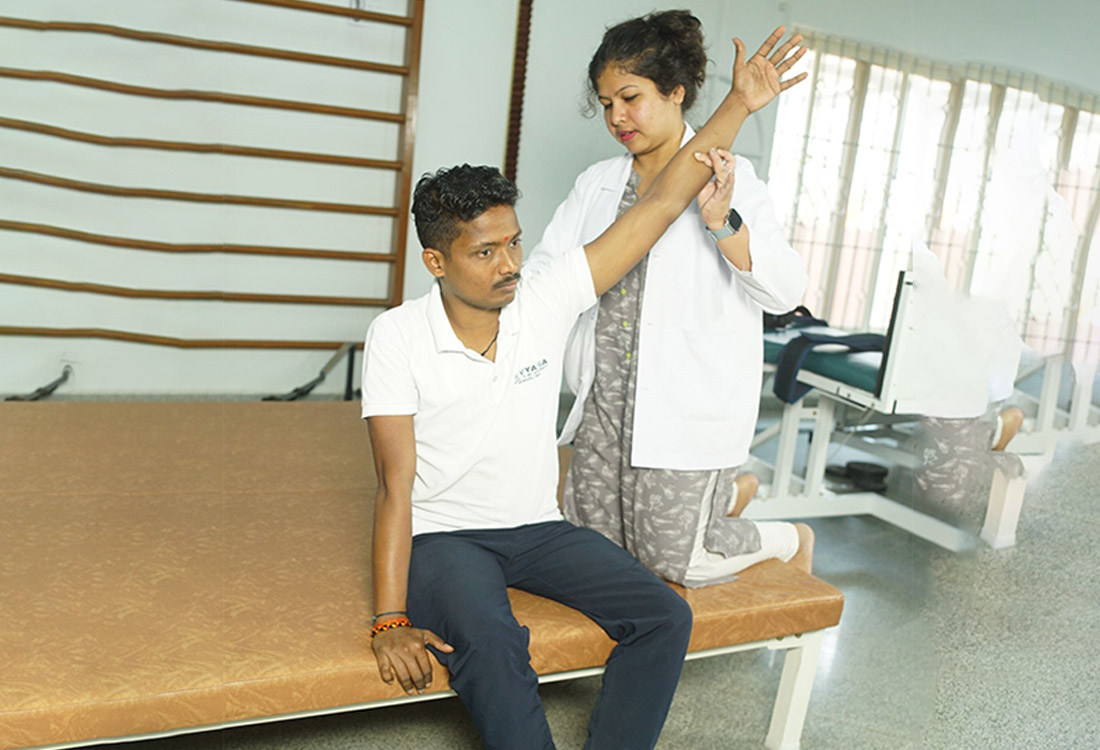

Neural mobilisation techniques
Neural mobilisation is a movement based therapy applied manually to mobilise and thereby activates a range of mechanical and physiological responses in nervous tissue such as neural sliding, pressurisation, elongation, tension and changes in intraneural microcirculation and nervous impulse movement. This technique is effective in relieving neuropathic pains.
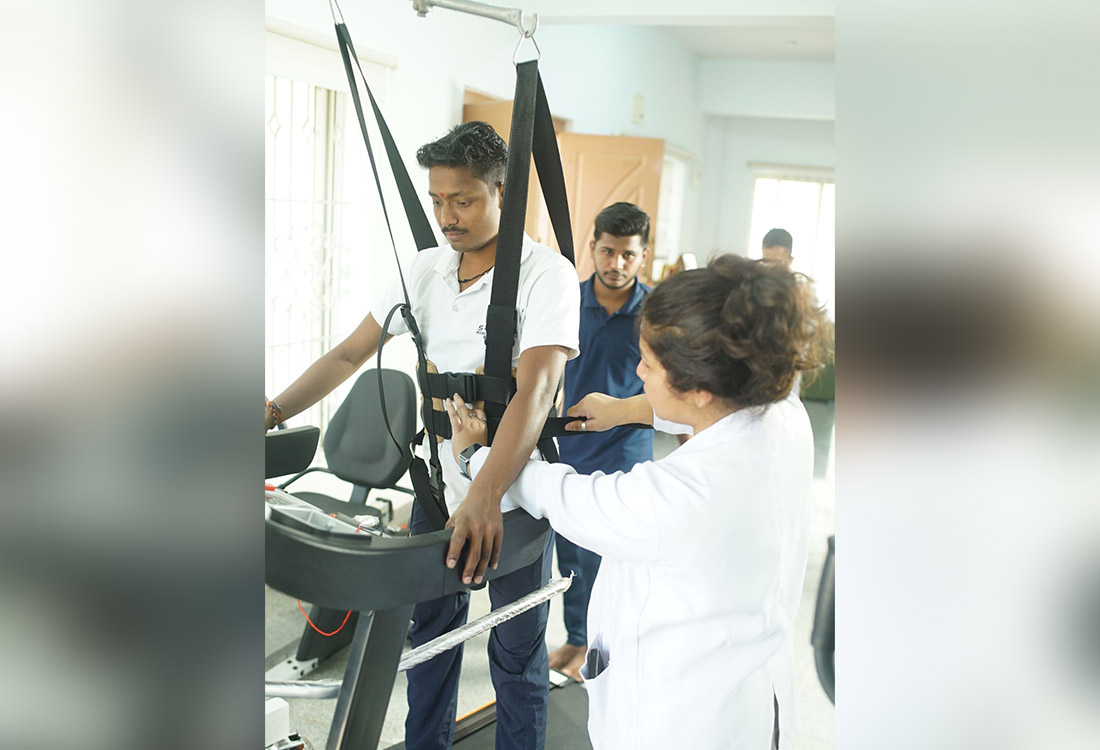
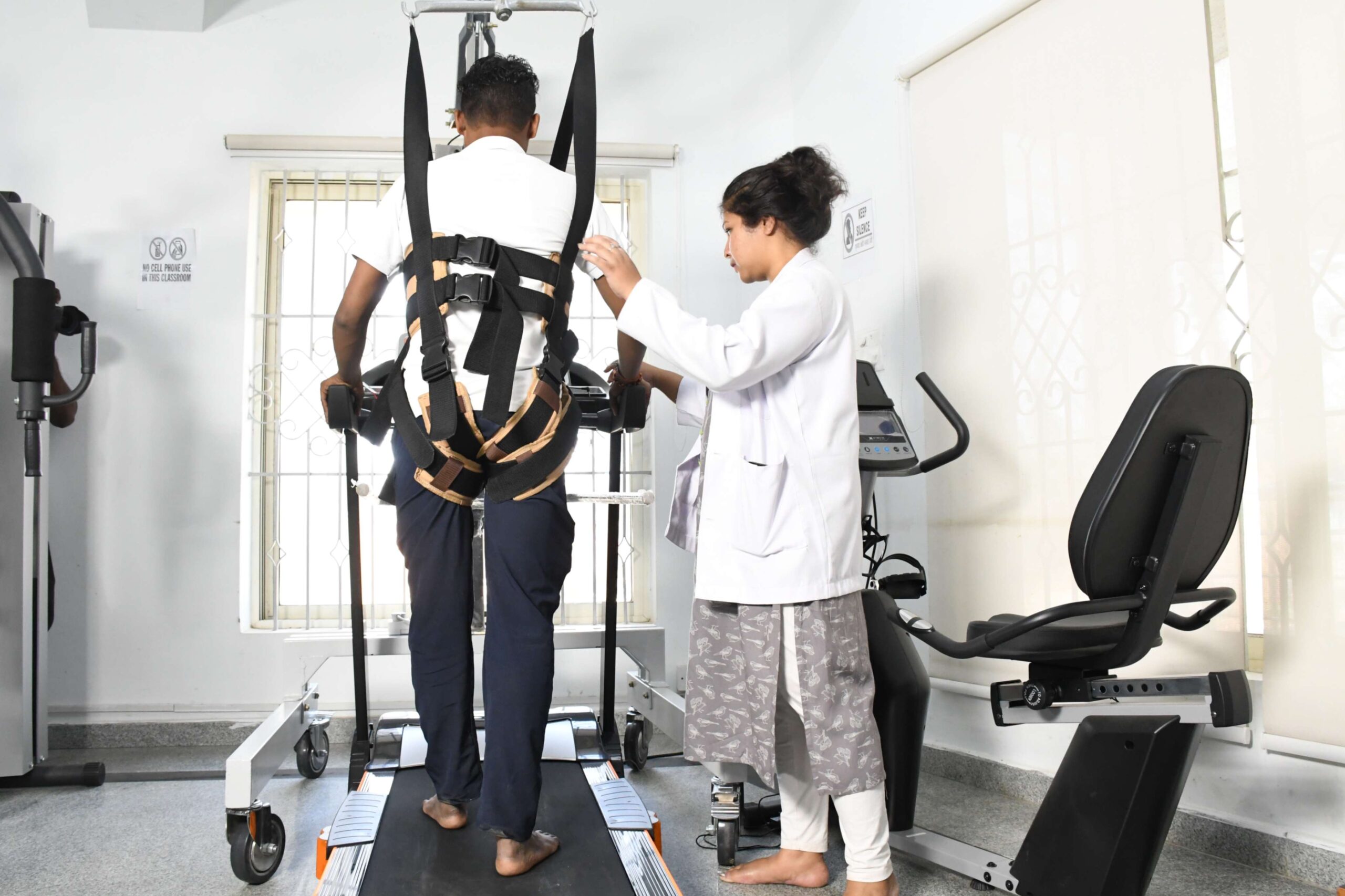
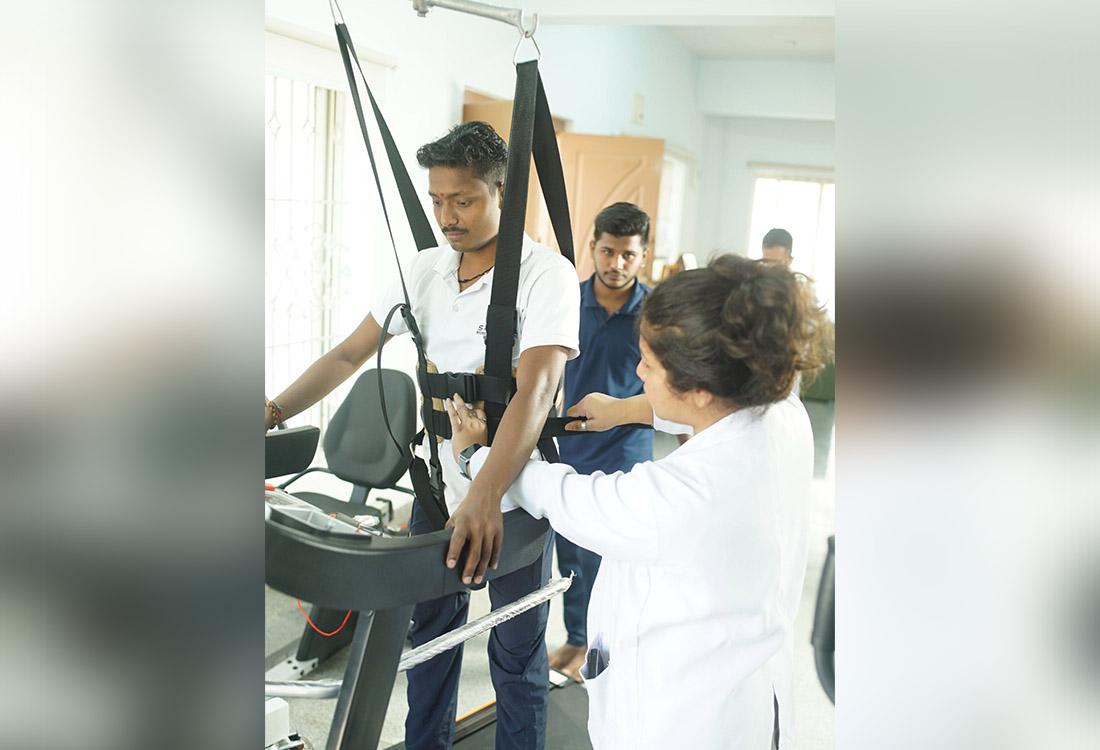
BWSTT(Body Weight Supported Treadmill Training)
Using treadmill training in conjunction with partial body weight support (BWS) has been one approach to retrain walking. For treadmill walking, the individual is partially suspended in a harness from the equipment frame (see photo) or from the ceiling to lessen weight bearing and give postural support. As postural control, balance, and coordination start to improve, the amount of support can be gradually reduced.
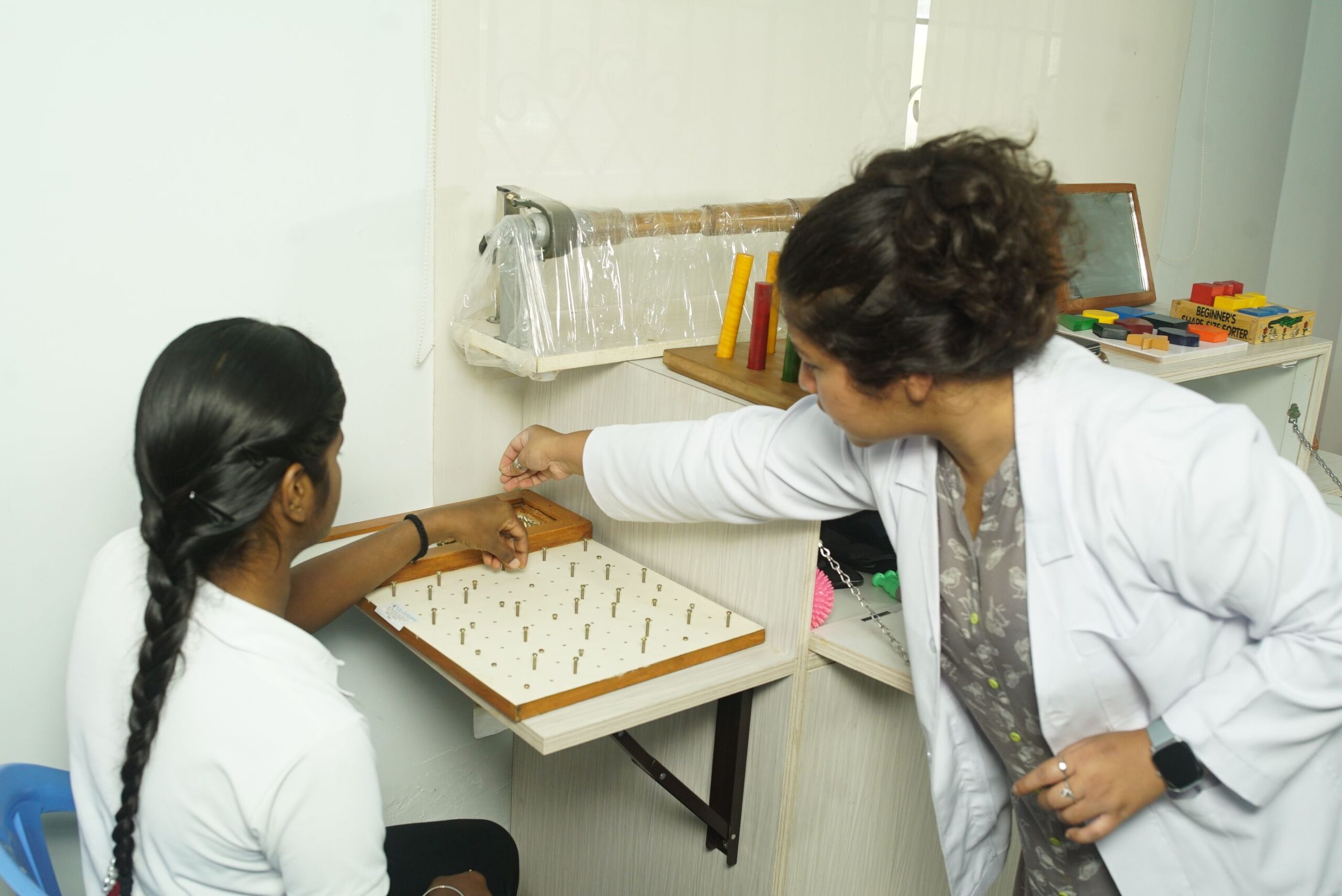
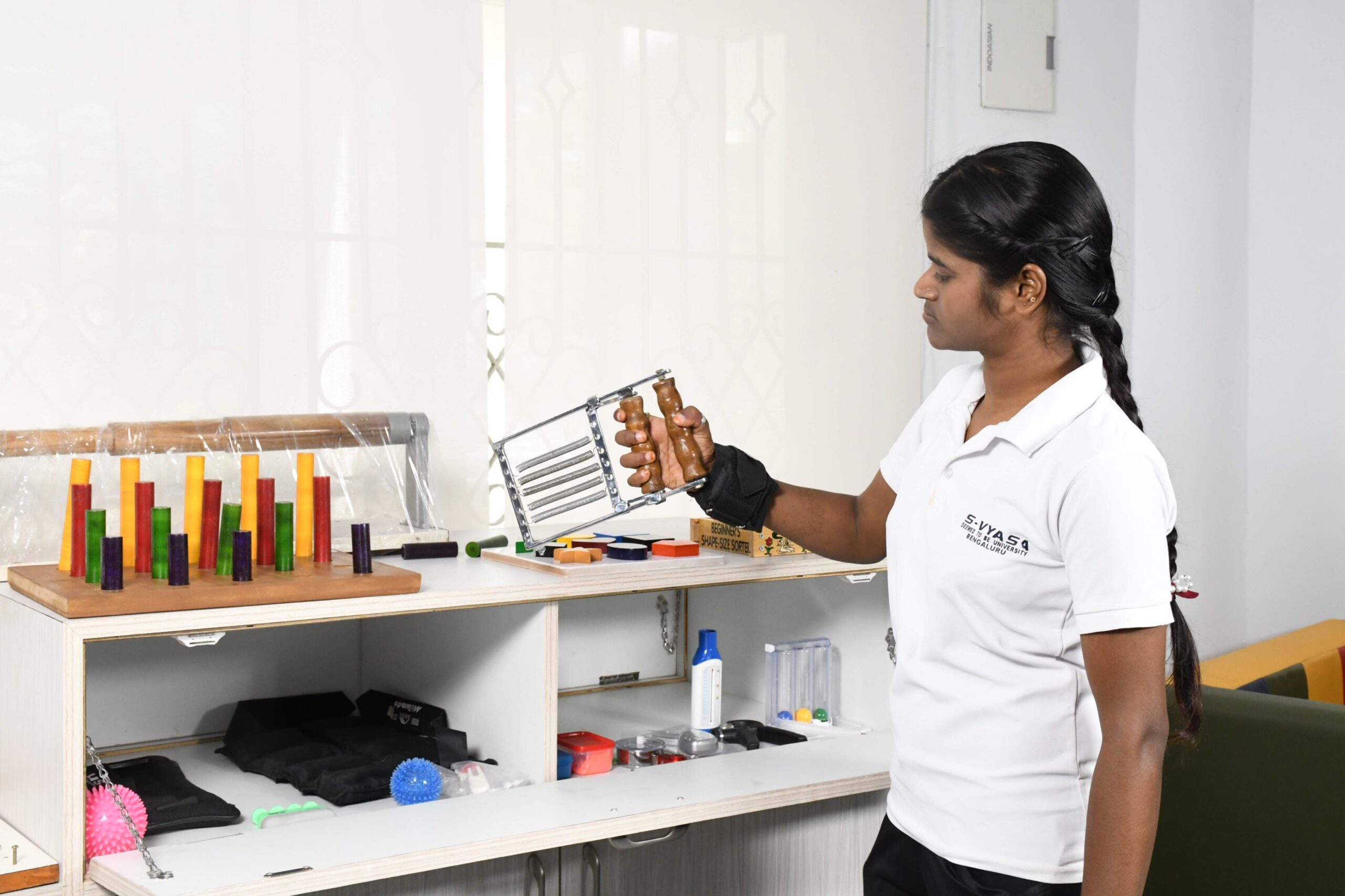
Hand Functions Training
Hand rehabilitation, also called hand therapy, is a group of assessments and interventions aimed at testing and restoring hand function after injury or paralysis. It aims at reducing pain, improving range of motion, grip strength, fine motor skills, coordination and dexterity, training patients to use adaptive devices, thereby promoting independence and enhancing quality of life..
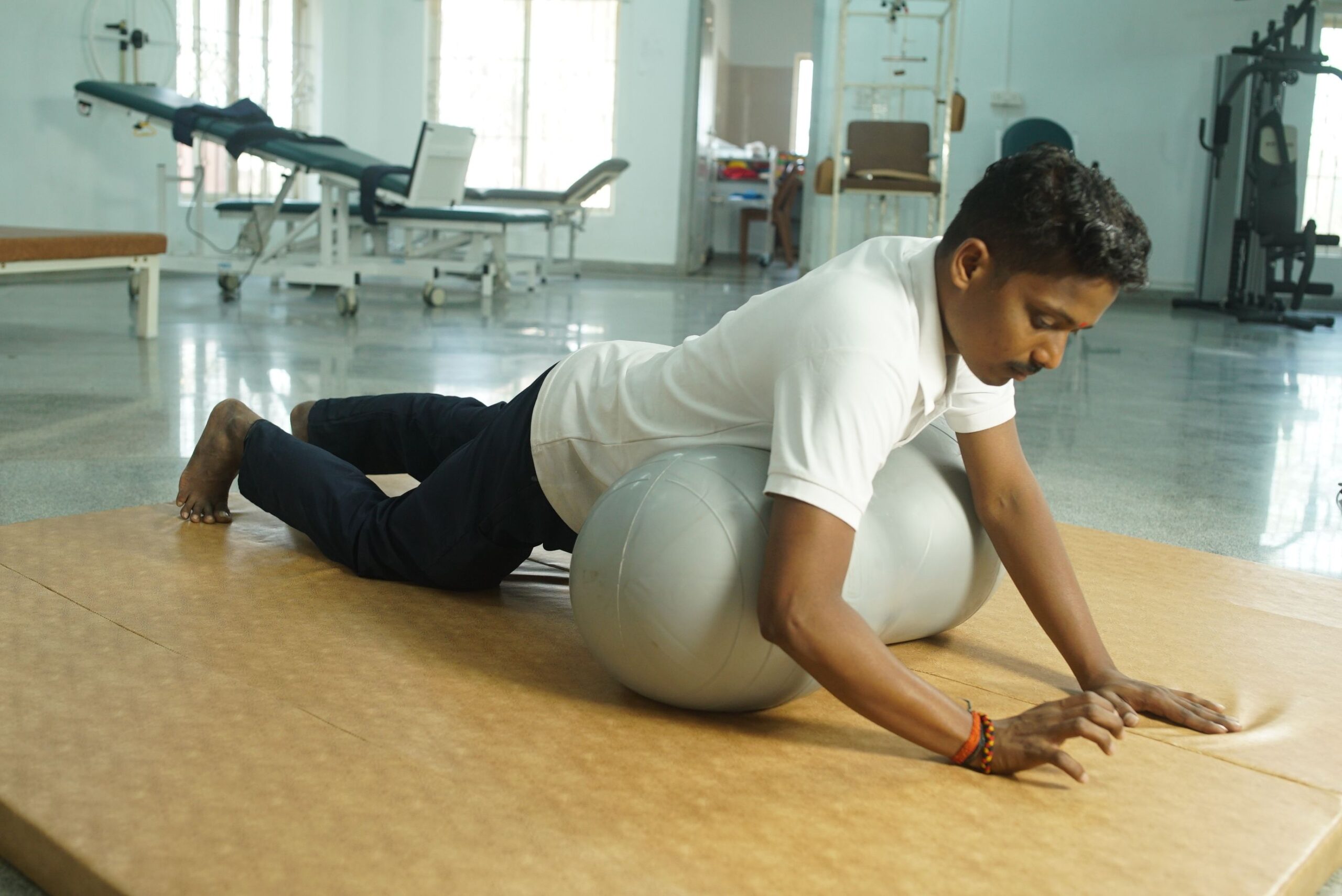

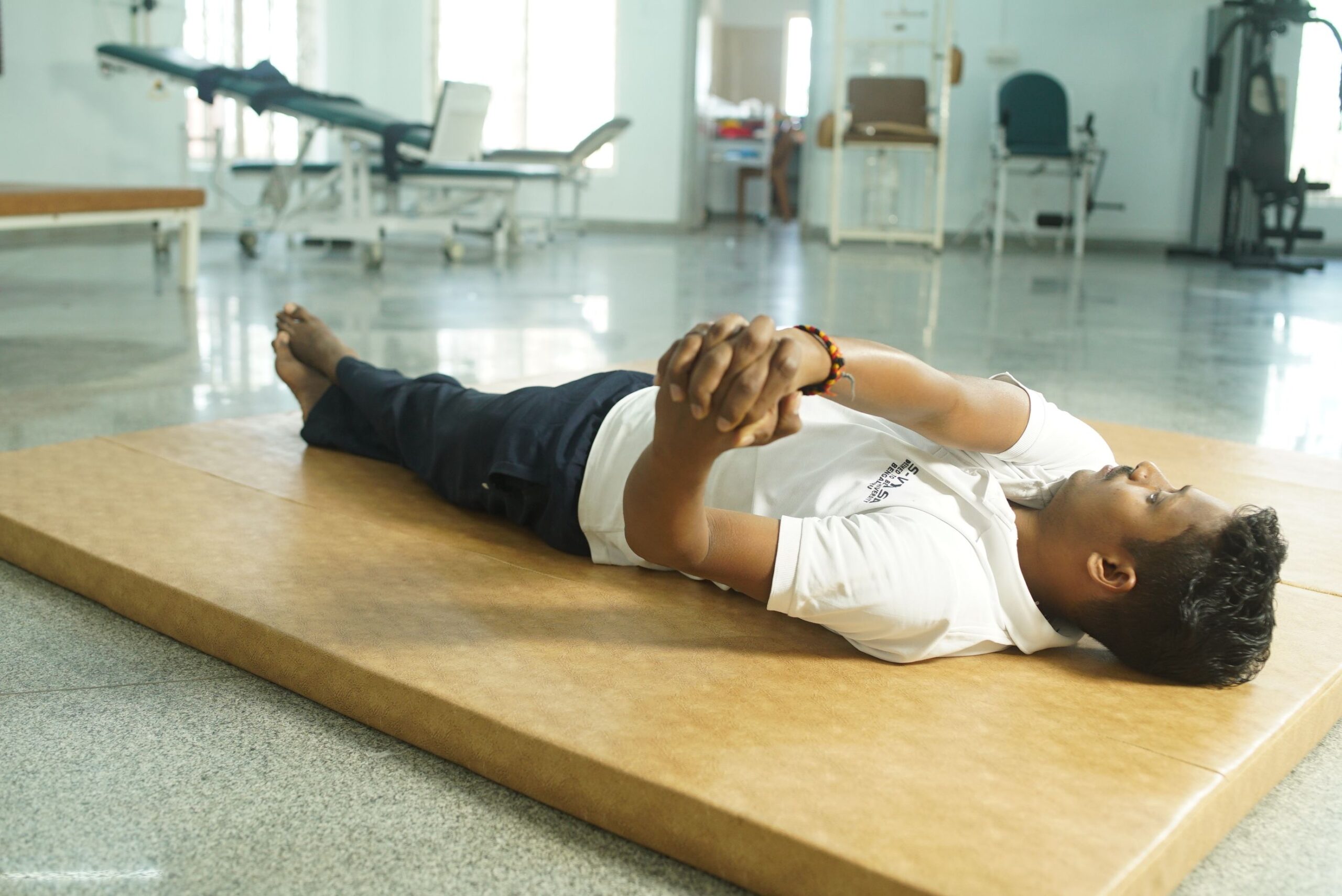
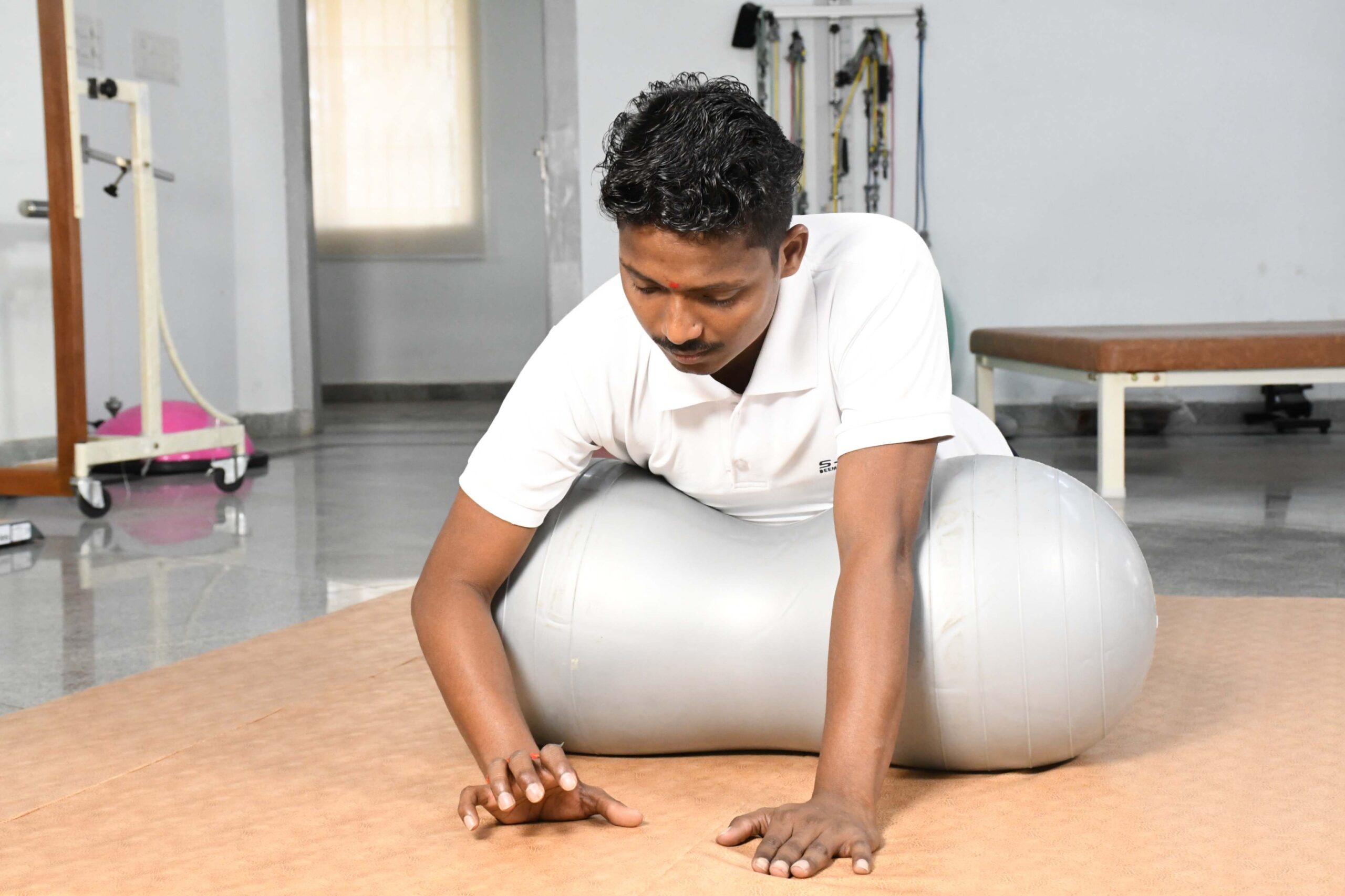
Mat exercises
Mat activities/ exercises include the practice of basic transitioning and transfers skills, and enables a patient with neurological disorders to strengthen the arm and core muscles, ultimately aiming at attaining an erect posture independently.
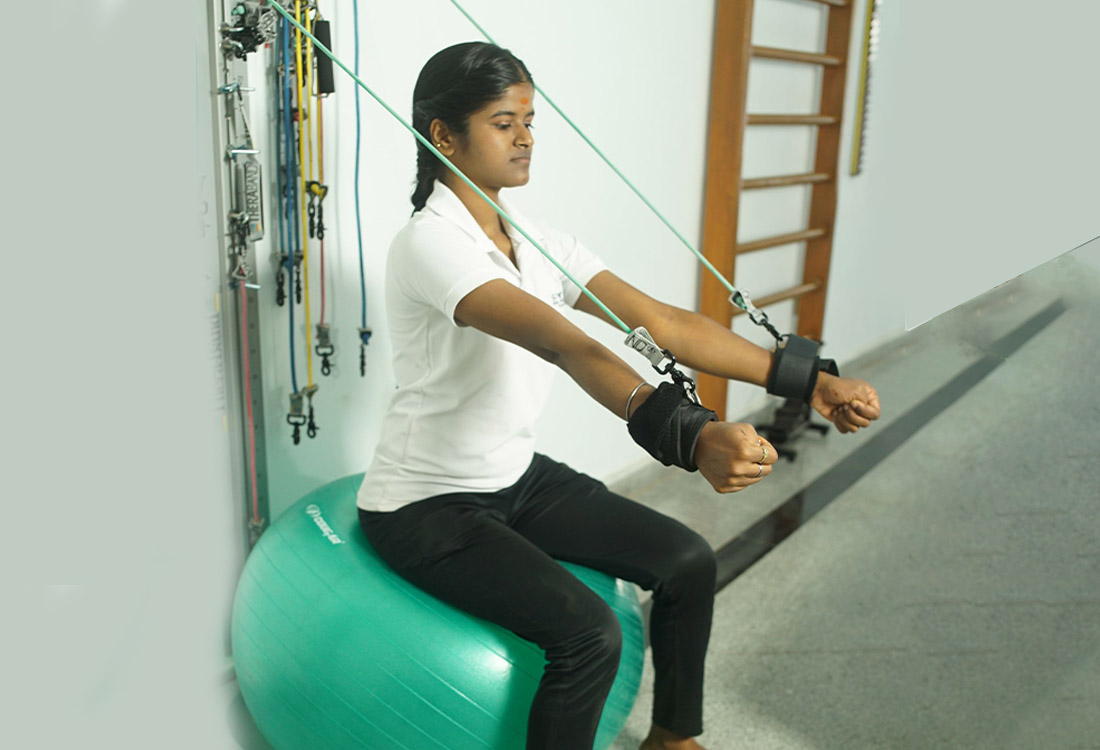
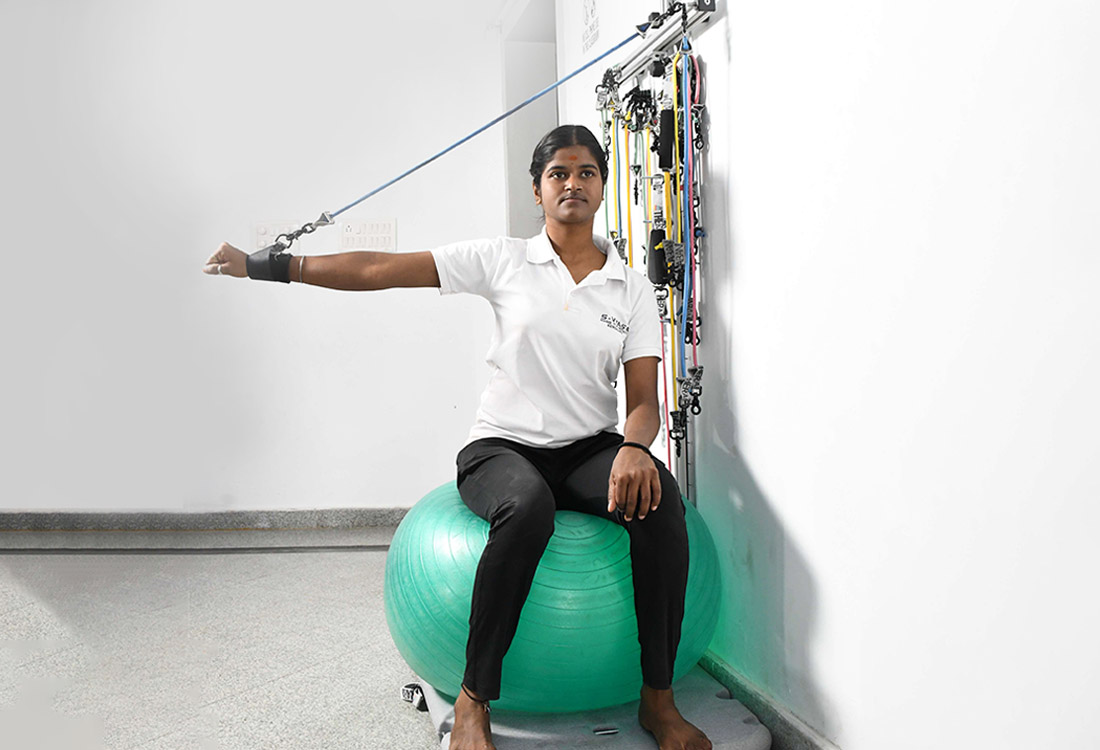
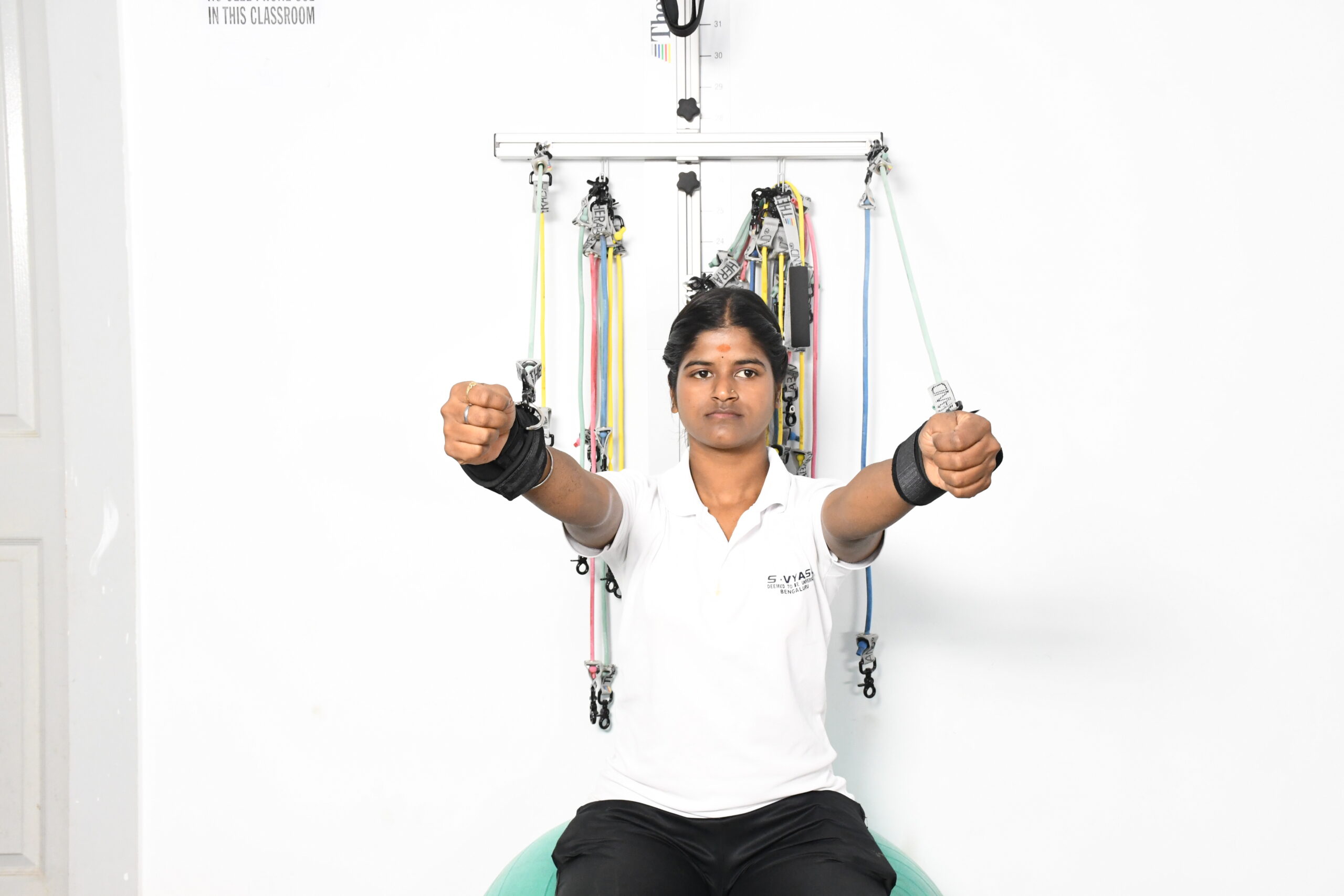
Theraband Station
Resistance bands known as therabands are adaptable and can be utilized for rehabilitation, flexibility exercises, and strength training. They are available in 8 different colors that offer different resistance, which can be administered as per the recommendation and progression levels.
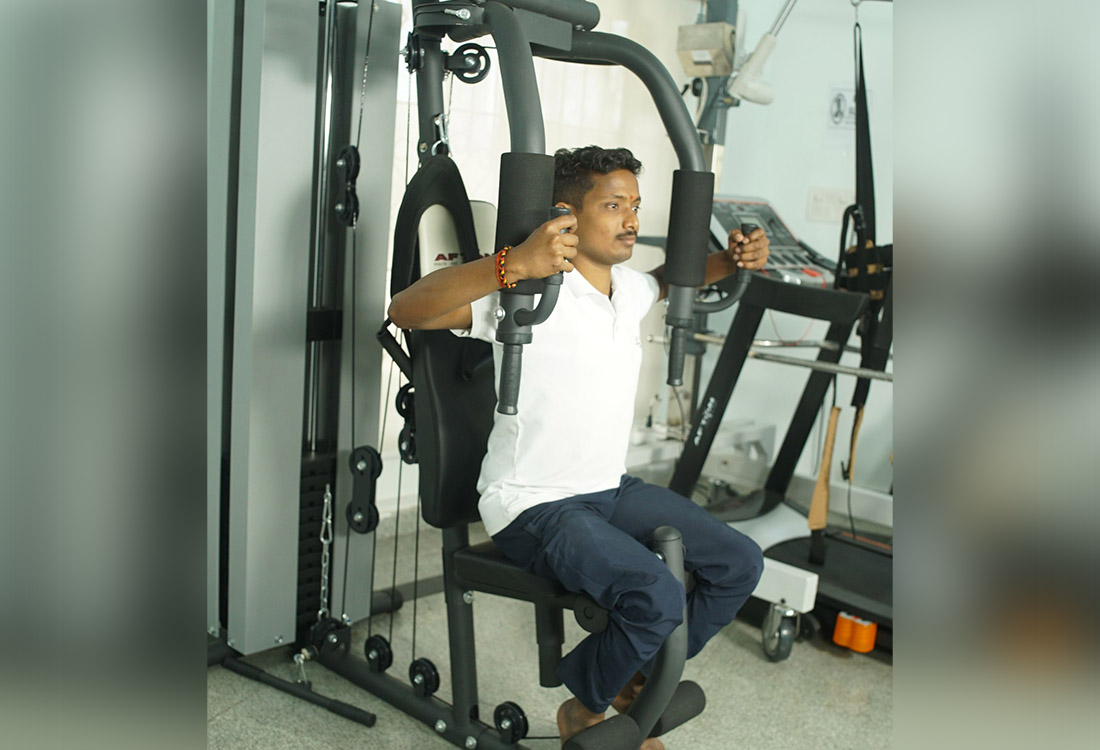

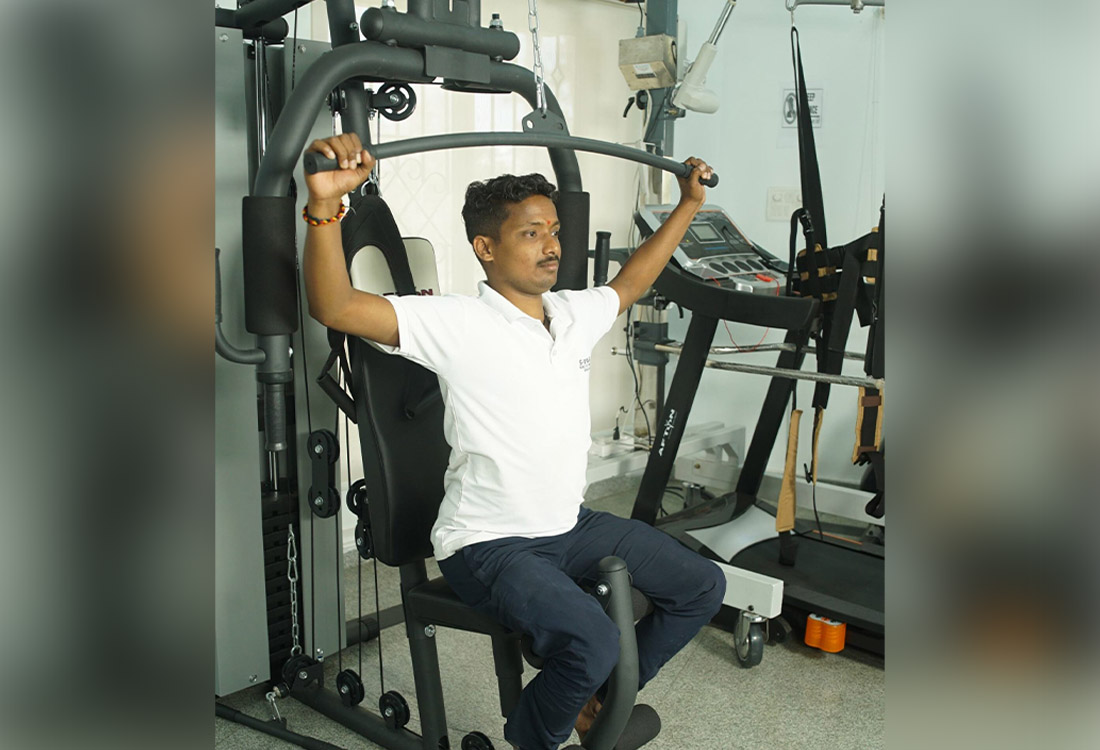
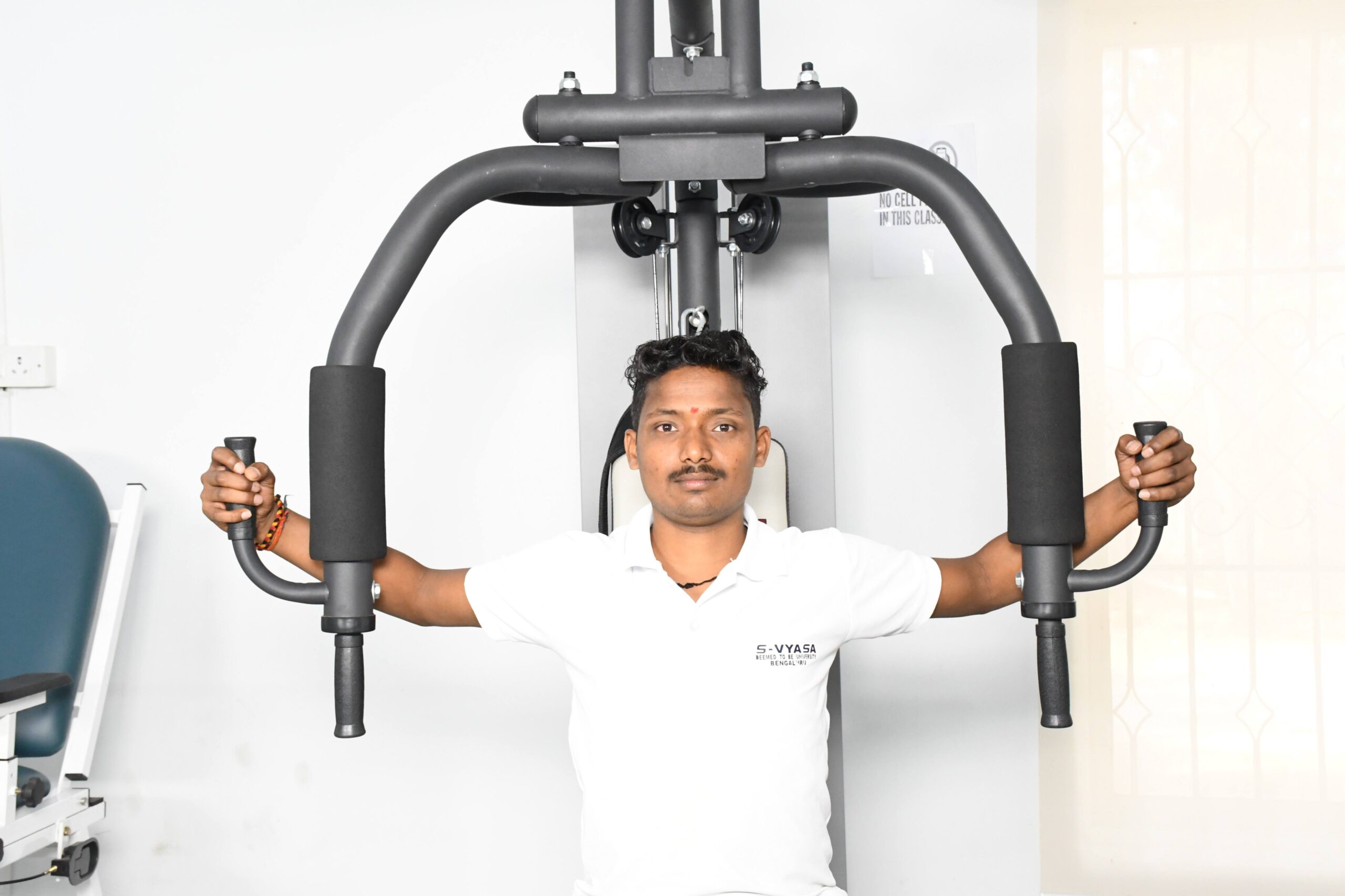
Multi Gym Unit
A multi gym unit can be used for advanced strength training, primarily aiming on resistance training of upper limb, upper back and lower limb muscles.
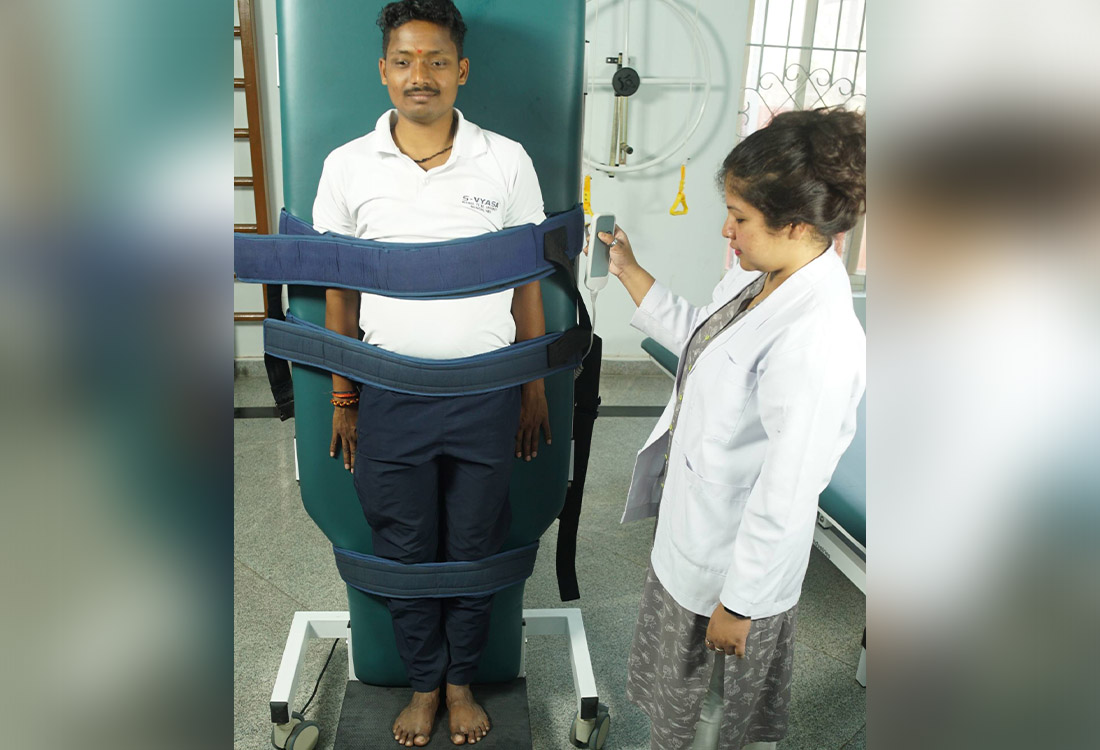
Tilt table
Tilt tables are well secured with straps recommended for attaining a vertical orientation, for the patients who have been bedridden for chronic periods. Tilt table standing reduces the symptoms of orthostatic hypotension, and ensures weight bearing and spasticity reduction in the lower limb muscles. It is also a prerequisite before one progresses to independent standing and walking.